Unveiling Jeddah’s history: 25,000 artefacts unearthed in landmark project – Dailynewsegypt


Saudi Arabia’s Historic Jeddah District Program, in collaboration with the Heritage Commission, has announced the exciting discovery of 25,000 ancient artefacts dating back to the early Islamic era. This landmark project sheds new light on the rich history of this UNESCO World Heritage site, bolstering its cultural and touristic significance.
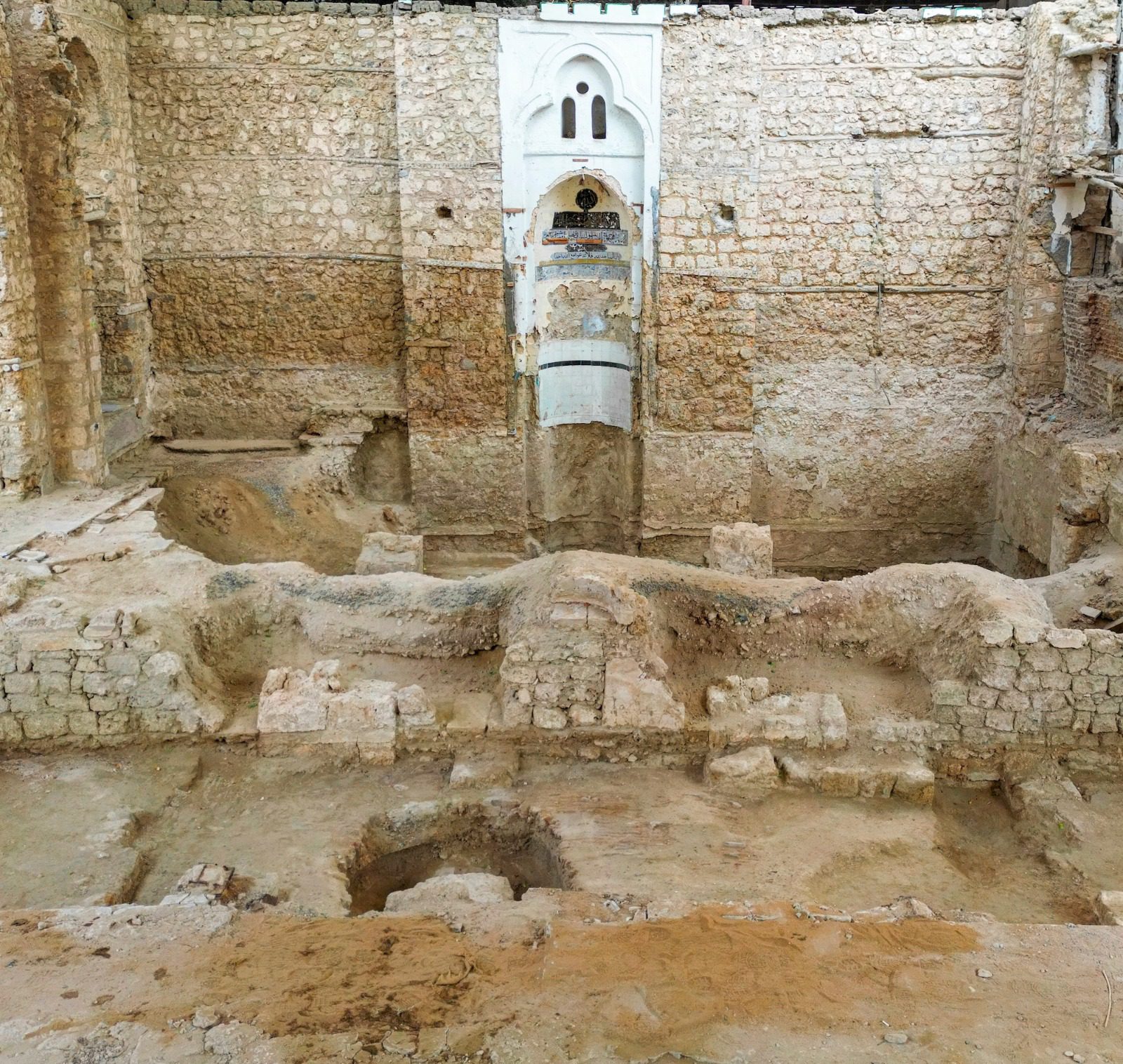
The discoveries stem from meticulous archaeological surveys and excavations conducted across four key locations: Othman bin Affan Mosque, Al-Shona, the Eastern Moat, and a segment of the Northern Wall. This initiative falls under the framework of the ambitious Historic Jeddah Revival Project, launched by Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman.
A Treasure Trove of History:
The unearthed artefacts paint a vivid picture of Jeddah’s vibrant past. Over 11,000 pottery sherds, 11,000 animal bones, and nearly 2,000 shells offer insights into daily life and trade practices. Building materials, glass artefacts, and metal objects further enrich the understanding of construction techniques and artistic expressions.
Othman bin Affan Mosque: A Journey Through Time:
Excavations at the mosque revealed layers of history spanning across centuries. Artifacts dating back to the early Islamic era (7th-8th centuries AD) were found, alongside evidence of Umayyad, Abbasid, Mamluk, and modern influences. Interestingly, ebony pillars flanking the Mihrab were identified to be from Ceylon Island, highlighting Jeddah’s extensive trade networks.
Unveiling Diverse Connections:
The discovered fragments include a variety of ceramic vessels and high-quality porcelain, some originating from China’s Jiangxi province (16th-19th centuries AD). Similarly, Al-Shona yielded European, Japanese, and Chinese pottery sherds from the 19th and 20th centuries AD, showcasing diverse cultural interactions.
Beyond Artifacts: Tombstones and Archival Riches:
Several Mangabi stone, marble, and granite tombstones were unearthed, bearing inscriptions potentially dating back to the 8th-9th centuries AD. These are currently under meticulous study by specialists. Additionally, over 984 historical documents, including maps and drawings, were meticulously gathered through international archival research, providing invaluable context for the archaeological finds.